Hallucinogen Addiction Treatment at Crestone Wellness
In recent years, the therapeutic potential of hallucinogens has garnered increasing attention in the field of mental health care.[1] Hallucinogenic substances, while often associated with profound experiences and altered states of consciousness, can also lead to detrimental patterns of abuse and dependency. Understanding and navigating these intricacies requires a specialized approach that acknowledges both the potential therapeutic benefits and the risks associated with misuse.
- Hallucinogens, also called psychedelics, alter perception, mood, and cognition by affecting neurotransmitter systems in the brain, primarily serotonin receptors.
- Common hallucinogens include LSD, psilocybin, DMT, mescaline, MDMA, and ketamine, each with its unique effects and duration.
- While not typically leading to physical addiction or withdrawal, hallucinogen abuse can result in problematic patterns of use and negative consequences, such as psychological distress, impaired functioning, and co-occurring mental health disorders.
- Overcoming hallucinogen abuse involves exploring evidence-based, holistic modalities like Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT), Art Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT), and others to address underlying psychological factors and promote recovery.
What Are Hallucinogens?
Hallucinogens, also known as psychedelics or hallucinogenic drugs, are a class of psychoactive substances that alter perception, mood, and cognition.[2] These substances can induce profound alterations in sensory experiences, leading to visual and auditory hallucinations, as well as changes in thought patterns and emotions.
Common examples of hallucinogens include LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide), psilocybin (found in certain mushrooms), DMT (dimethyltryptamine), mescaline (found in peyote and certain cacti), and MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine), often referred to as ecstasy or molly.[3] Each substance within this class has its own unique effects and duration of action.
Hallucinogens primarily work by affecting neurotransmitter systems in the brain, particularly serotonin receptors.[4] By modulating serotonin signaling, these substances can induce altered states of consciousness characterized by enhanced sensory perception, distorted time perception, and profound introspection.
Hallucinogen Addiction and Abuse
While hallucinogens are not typically associated with physical dependence in the same way as substances like opioids or alcohol, they can still lead to problematic patterns of use.
As with all substance abuse, hallucinogen use can be accompanied by a range of negative consequences and side effects:[5]
Psychological distress:
While some people may have positive experiences with hallucinogens, others may encounter profound psychological distress, such as anxiety, paranoia, or even psychosis, especially in vulnerable individuals or in the context of an unsupportive environment.
Flashbacks:
Some people who have used hallucinogens may experience spontaneous and recurrent hallucinogenic effects, known as “flashbacks,” even long after the drug has left their system.
Impaired functioning:
Chronic misuse of hallucinogens can impair cognitive function, memory, and decision-making abilities, leading to difficulties in work, school, or social relationships.
Risk of harm:
Hallucinogen abuse can increase the risk of accidents, injuries, or self-harm, particularly if you engage in risky behaviors while under the influence of these substances.
Co-occurring mental health disorders:
Hallucinogen abuse often co-occurs with other mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, or trauma-related conditions, further complicating the treatment process.
Hallucinogens Addiction

Hallucinogen Quick Reference Chart
Drug Category
Commercial & Street Names
DEA Schedule
Administration
What Are Some Common Hallucinogens?
Some common types of hallucinogens include:[6]
LSD:
A potent synthetic compound known for its profound effects on perception, mood, and consciousness.

Psilocybin:
Found in certain species of mushrooms, psilocybin produces hallucinogenic effects similar to LSD but with a shorter duration of action.

DMT:
A naturally occurring psychedelic compound found in plants and animals, often consumed in traditional ayahuasca brews.

Mescaline:
Found in peyote cactus and certain other cacti, mescaline produces hallucinogenic effects and has been used ceremonially by indigenous cultures for centuries.

MDMA:
While primarily known as a stimulant, MDMA can also produce mild hallucinogenic effects, leading to altered perception and enhanced empathy.
Ketamine:
Originally developed as an anesthetic, ketamine has dissociative and hallucinogenic properties and is sometimes used illicitly for recreational purposes or as a therapeutic agent in controlled settings.
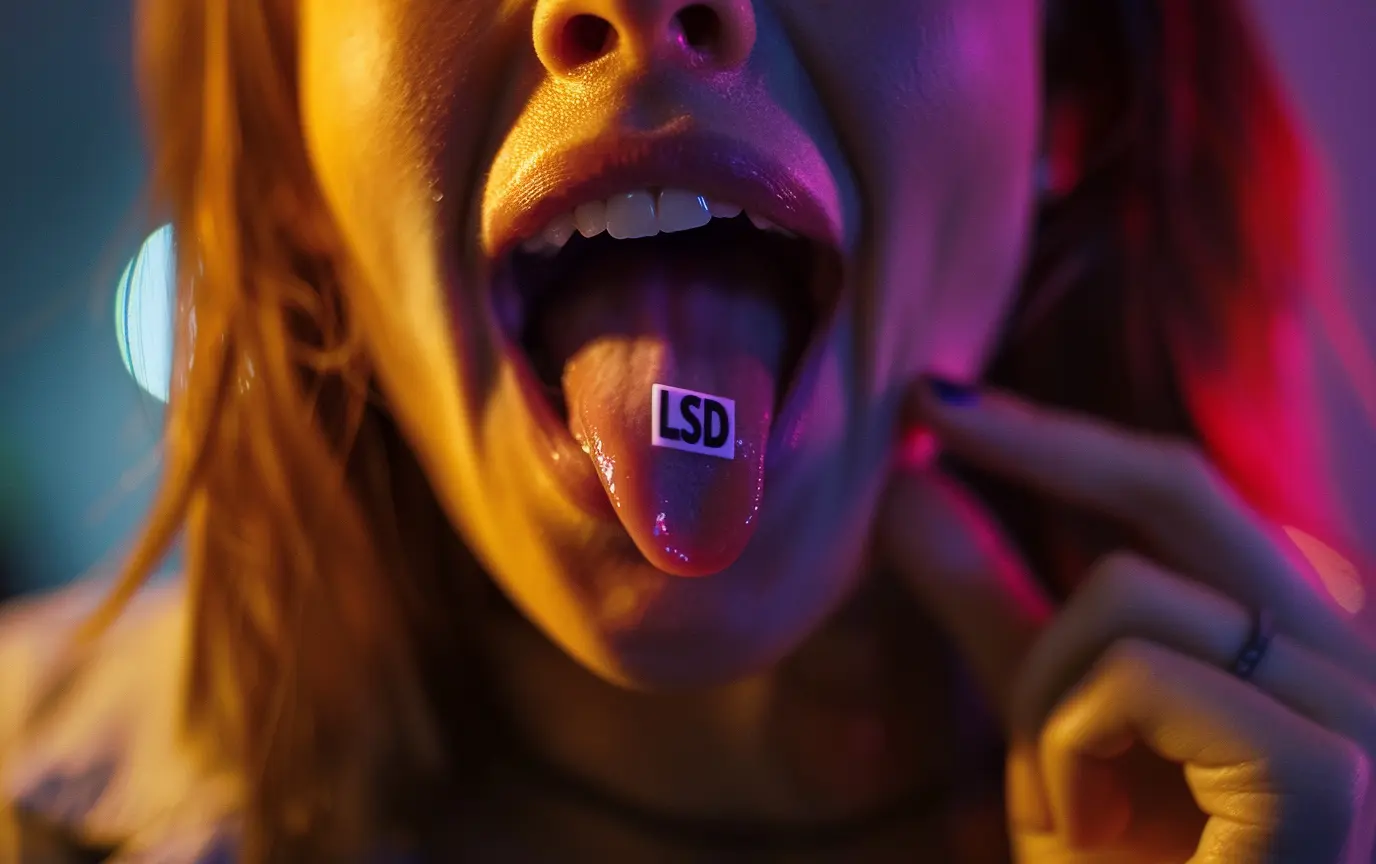
Are Hallucinogens Addictive?
Hallucinogens like LSD and psilocybin don’t typically lead to physical addiction or withdrawal symptoms. However, some people may develop a psychological dependence, craving the unique experiences they offer – and abusing hallucinogens can still result in the development of a substance use disorder.[7]
Tolerance can also develop as well, leading to increased dosage and potential risks. While less common than addiction to some other substances, problematic use can still occur and may require comprehensive treatment addressing underlying psychological factors and promoting healthier coping strategies.
What Are My Options for Hallucinogen Abuse Treatment?
Overcoming hallucinogen abuse and starting your journey of recovery involves exploring a variety of evidence-based, holistic modalities:
Frequently Asked Questions About Hallucinogen Abuse Treatment
Is detoxification necessary for hallucinogen abuse treatment?
Detox, or detoxification, is not typically necessary for hallucinogen abuse treatment due to the lack of physical dependence associated with these substances. However, medical supervision may be provided to ensure the individual’s safety and comfort during the early stages of treatment.
How does therapy address underlying issues contributing to hallucinogen abuse?
Therapy in hallucinogen abuse treatment aims to address underlying psychological factors contributing to substance misuse. Through various modalities such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), and trauma-informed approaches, you can explore and process emotions, trauma, and maladaptive coping mechanisms, fostering insight and resilience in recovery.
How do I know if I or a loved one need hallucinogen abuse treatment?
How do I find a treatment program for hallucinogen abuse?
Finding a hallucinogen abuse treatment program involves researching available options, such as residential treatment centers, and considering factors such as location, cost, and treatment approach. Seeking recommendations from healthcare professionals, support groups, or trusted sources can also help in identifying suitable treatment programs. Additionally, many treatment facilities offer online resources and helplines to assist individuals in finding the right program for their needs.
Sources
[1] Gregorio, D. D., Aguilar-Valles, A., Preller, K. H., Heifets, B. D., Hibicke, M., Mitchell, J., & Gobbi, G. (2021). Hallucinogens in Mental Health: Preclinical and Clinical Studies on LSD, Psilocybin, MDMA, and Ketamine. Journal of Neuroscience, 41(5), 891–900. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1659-20.2020 on June 5, 2024
[2] Nichols, D. E. (2016). Psychedelics. Pharmacological Reviews, 68(2), 264–355. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.115.011478 on June 5, 2024
[3] National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2023, April). Psychedelic and Dissociative Drugs. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/psychedelic-dissociative-drugs on June 5, 2024
[4] Raj, P., Rauniyar, S., & Sapkale, B. (2023). Psychedelic Drugs or Hallucinogens: Exploring Their Medicinal Potential. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.48719 on June 5, 2024
[5] National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2023, April). Psychedelic and Dissociative Drugs. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/psychedelic-dissociative-drugs on June 5, 2024
[6] Hallucinogens. (n.d.). Www.dea.gov. https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/hallucinogens on June 5, 2024
[7] National Institute on Drug Abuse. (2023, April). Psychedelic and Dissociative Drugs. National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://nida.nih.gov/research-topics/psychedelic-dissociative-drugs on June 5, 2024




